ABSTRACT
There are several theories and styles of leadership, as well as several approaches to studying it. This article studies the emergence and evolution of Green Servant Leadership, advocating for collaborative research to explore its development from 2012 to 2023. Utilizing bibliometrics and using VOS Viewer software, we analyze metadata from 33 publications available on Scopus. Our findings indicate a global interest in various aspects of green servant leadership, with a notable surge in research volume in recent years. The study underscores the importance of these insights for future researchers, facilitating collaborative networks among institutions, countries, and authors who have contributed significantly to this field. Researchers should collaborate more to better understand Green Servant Leadership, leveraging bibliometrics and tools like VOS Viewer for comprehensive analysis. They should prioritize investigating evolving trends, fostering global networks, and advancing knowledge within the context of environmental sustainability and the social sciences.
Keywords: Bibliometric analysis, Servant leadership, Bibliometric coupling, VOS Viewer, Scopus.
INTRODUCTION
Robert K. Greenleaf originally coined the term “servant leadership”. Spears (1995) summarizes that Greenleaf identified certain leaders with servant attributes who are motivated to serve others. They aspire to lead in a way that meets the needs of those they serve. Due to its close relationship with transformational and ethical leadership, servant leadership has often been considered an overlapping concept or even a sub-dimension of ethical leadership.
Tuan (2018) argued that servant leadership is specifically geared toward the environment, following on from van Dierendonck (2011), with a framework involving several attributes, such as providing guidance, empowering, and developing employees to become pro-environmental citizens, and exhibiting authenticity, humility, interpersonal acceptance, and stewardship of employees’ efforts to contribute to environmental sustainability. A servant leader is someone who is driven by a desire to serve others while leading them (Liden et al., 2014; 2015) and prioritizes the interests of other individuals and the larger community (Schaubroeck et al., 2011). Servant leaders are also role models for others, embodying empathy, altruistic values, and a deep commitment to group goals (Whittington, 2017). Servant leaders demonstrate moral responsibility not only toward the growth and success of the organization they lead (Whittington, 2017), but also toward the wellbeing of its stakeholders, including employees and the local community (Ehrhart, 2004; Hussain et al., 2023).
While servant leadership undoubtedly involves influencing outcomes by prioritizing the needs of others and serving them (Greenleaf, 2002), there has been a shift in its conceptualization from a broad focus on influencing outcomes in diverse contexts to a more specific focus on utilizing the same set of servant behaviors to achieve a particular target (Afsar et al., 2018). Robertson & Barling (2017) propose expanding the scope of servant leadership to include environmental targets and exploring the potential role of environmental servant leadership in driving specific environmental outcomes. In recent times, researchers have introduced the concept of Environmental-Specific Servant (ESS) leadership, which expands the scope of target-specific servant leadership to include environmental sustainability. ESS leaders are defined as those who act as role models by promoting pro-environmental values and demonstrating a deep commitment to green goals, while also serving and assisting others, including employees, to contribute toward the sustainability of the organization they lead and the broader community (Tuan, 2018). Essentially, ESS leadership is a form of servant leadership that centers on promoting green behaviors and is a particular style of green leadership, a leadership style relating to the extent to which managers display a willingness and commitment to promoting environmentally friendly practices and implementing changes, leading to competitive advantage (Lee et al., 2014; Miller & Friesen, 1983).
In addition, ESS leadership can serve as a leadership approach promoting green behavior that complements the dominant approach of green transformational leadership in the green management literature (Robertson & Barling, 2017). Hoch et al. (2018) found that servant leadership appears to involve a greater degree of conceptual and empirical differences than transformational leadership. The motivation of servant leaders is focused on the development of their followers as an end goal. In contrast, transformational leaders prioritize meeting the needs of their followers as a means to achieve the organization's objectives (Eva et al., 2019; van Dierendonck et al., 2014). According to Karakas & Sarigollu (2013), servant leadership is also characterized by a sense of calling and responsiveness to community needs.
We recognize the necessity for an extensive and cohesive analysis of bibliometric data to identify the essential trends and advancements in green servant leadership research over time. This review aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the key dynamics and evolution within the field of green servant leadership and identify primary research areas, current trends, and future directions within the field. To achieve this objective, we have employed the bibliometric review technique to address the following questions:
1. What is the historical progression and evolution of servant leadership research?
2. What are the main research streams or thematic areas within the field of green servant leadership research?
3. Which specific channels, such as journals, articles, authors, institutions, and countries, exert the greatest influence on green servant leadership research?
4. Is there an established collaborative network among authors across different countries for conducting green servant leadership research?
The literature on servant leadership has undergone three phases: conceptual definition and construct development, scale creation and investigation of antecedents/outcomes, and modeling mediating mechanisms and boundary constraints. Despite some meta-analyses, a comprehensive overview of research on (green) servant leadership is absent. A holistic bibliometric review tracing its evolution, key dynamics, origins, and progress is crucial to better understanding the future of the field. With this article, its authors aim to pinpoint potential areas and gaps in previous research while offering technical considerations for future researchers.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Green servant leadership is a relatively new concept that combines the principles of servant leadership with environmental stewardship. It is a style of leadership that seeks to serve others while also minimizing negative impacts on the environment and has been defined by researchers in several ways.
Green servant leadership involves leaders who prioritize the wellbeing of their followers, their organization, and the environment in their decision-making and actions. Such leaders seek to serve the needs of their followers while also promoting sustainable practices and reducing the organization's ecological footprint (Sher & Nawaz, 2021).
For Sosik & Jung (2011), green servant leaders prioritize the needs and wellbeing of their followers and also consider the long-term impact of their decisions on the planet. Siddiquei et al. (2021) define green servant leadership as “a leadership approach that emphasizes serving the wellbeing of followers, while also promoting the wellbeing of the environment and addressing sustainability challenges”. Other concepts such as Servant Leadership, Environment Considerations, and Green Human Resource Management (GHRM) also share a common objective of promoting and inspiring the community to work toward the preservation of the environment and pursue common interests (Sher & Nawaz, 2021).
The available literature shows that servant leadership is associated with modifying and shaping the behavior of employees by utilizing stakeholder management, which is grounded in the stakeholder theory (Neubert et al., 2016). Organizations that prioritize environmental sustainability encourage their employees to adopt green practices and achieve high levels of economic, social, and environmental performance. To achieve this, they employ green servant leadership, foster a helpful attitude toward environmental concerns, and implement GHRM practices (Sher & Nawaz, 2021). Green servant leadership is a form of leadership that stems from an individual’s desire to lead and to connect their personal beliefs with meeting the needs of others. It emphasizes the importance of respecting green considerations and preserving the environment for the benefit of future generations (Tuan, 2020).
The approach of green servant leadership aims to motivate employees to achieve pro-environmental targets set by the company, while also ensuring that team members work according to the organization's chosen environmental profile (Tuan, 2021). The success of environmental initiatives depends on the effectiveness of their leaders (Robertson & Barling, 2017). Servant leadership is a leadership philosophy that emphasizes the leader’s responsibility to serve the needs of their followers, rather than the leader’s self-interest or ambition (Liden et al., 2015). Servant leaders prioritize not only the interests of their team members but also the interests of the larger community they serve (Greenleaf, 1970). Servant leaders serve as role models by exemplifying empathy, altruistic values, and a strong commitment to the goals of their group (Whittington, 2017). One framework (van Dierendonck, 2011) of servant leadership attributes focuses on three key elements: directing, empowering, and developing employees to become pro-environmental citizens, and exhibiting authenticity, humility, interpersonal acceptance, and stewardship of employees’ pro-environmental contributions (Tuan, 2018).
Leaders who adopt this approach provide guidance and support to their employees to become environmentally responsible, while also fostering a culture of mutual respect and accountability toward environmental goals. Additionally, they lead by example, demonstrating the values they preach and valuing the contributions of their employees toward a more sustainable future. Servant leaders demonstrate a moral responsibility not only to the growth and success of their organization, as noted by Whittington (2017), but also to the needs and interests of its stakeholders, including its employees and community. Robertson & Barling (2017) proposed broadening the scope of servant leadership to include environmental concerns. They explored the potential impact of an environmentally focused version of servant leadership on achieving specific environmental goals.
The concept of green servant leadership was developed to integrate environmental considerations into an organization's operations and practices. This approach emphasizes the importance of leadership that is both environmentally responsible and focused on serving the needs of all stakeholders (Afsar et al., 2020). The green servant leadership approach aims to inspire employees to work toward achieving the organization’s pro-environmental goals. This is done while ensuring that team members serve in line with the organization's chosen environmental profile (Manz et al., 2011; Tuan, 2021).
According to Afsar et al. (2020), green servant leadership is built on four core principles of servant leadership: listening, empathy, healing and awareness. In addition to these core principles, green servant leadership also includes a focus on sustainability and environmental responsibility. This means that green servant leaders take steps to reduce their organization’s impact on the environment, such as reducing waste, conserving resources, and using eco-friendly products. Siddiquei et al. (2021) argue that green servant leadership can lead to several positive outcomes, including improved organizational performance, increased employee engagement, and a more sustainable approach to leadership. They also suggest several areas for future research, including the development of tools to measure green servant leadership and the examination of the relationship between green servant leadership and organizational outcomes. Overall, green servant leadership is a leadership approach that combines a focus on serving others with a commitment to sustainability and environmental responsibility (Afsar et al., 2018). It has the potential to benefit both individuals and the planet and is an area of growing interest and research in the field of leadership studies. Paesen et al. (2019) highlighted the positive impacts of servant leadership on various variables including organizational behavior, trust in leaders and organizations, performance at both organizational and team levels, organizational commitment, and employee satisfaction.
METHOD, DATA, AND ANALYSIS
This study is a work of bibliometric analysis, examining the field of green servant leadership by analyzing data lifted from the Scopus database. It analyzes all relevant publications on the topic across different disciplines within the Social Sciences Citation Index. This approach enables a structured analysis of the literature, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of the field and its key features.
Zupic & Čater (2015) usefully explain bibliometrics as a quantitative tool or measure for analyzing different aspects of publications, including journals, authors, keywords, countries, citations, and co-authors. To perform quantitative analysis, bibliometric analysis necessitates the utilization of visualization and mapping software (Cobo et al., 2011). Software plays a crucial role in extracting citation links and assessing the strength of these links. It also facilitates the analysis of bibliographic coupling, which involves examining connections based on authors, countries, citations, and sources.
SOFTWARE
Software packages such as VOS Viewer offer more than just descriptive statistics of publications. They also assist in analyzing complex associations between different characteristics of publications, such as citation analysis, citation links, and bibliographic coupling (van Eck & Waltman, 2010). VOS Viewer is specifically designed to create, visualize, and explore bibliometric maps (van Eck & Waltman, 2010). For this study, the authors inputted data in comma-separated value formats from citation databases Scopus. Once imported, VOS Viewer allows cleaning and preprocessing. This involves removing duplicates, filtering irrelevant or low-quality data, and standardizing data formats. The software constructs networks based on relationships such as co-authorship or keyword co-occurrence and generates interactive visualizations of these networks. Users can analyze these visualizations to identify clusters, assess centrality, and detect trends. VOS Viewer also offers customization options for tailored analyses. Researchers interpret results to better understand quantitative dynamics of discrete literatures, which can inform further research.
DATABASES
The researcher utilized the Scopus database to gather papers published in the English language between 2012-2023. Scopus was selected as the database of choice due to its user-friendly interface and its extensive coverage of journals that have a significant impact on the social sciences (Hussain et al., 2023), as well as because it encompasses both Institute for Scientific Information (ISI) and Scopus-indexed publications, ensuring a broad coverage of papers across various disciplines, including social sciences. It is considered to be a more comprehensive resource compared to the Web of Science, which includes only ISI-indexed journals (Fahimnia et al., 2015).
SEARCH STRATEGY
To gather all relevant publication data concerning research on green servant leadership from Scopus, search queries including the terms “green servant leadership” and “environmental-specific servant leadership” were employed. Searches encompassed the title, abstract, and keywords fields, with the publication year limited to 2023. The raw data was filtered by restricting the search parameters to specific criteria. This involved limiting the document type to journal articles, the source type to articles, and the language to English. Additionally, the filter for “selecting relevance” was applied to refine the results. The search yielded a total of 33 papers from the years 2012 to 2023. There was only one publication in 2012, but by 2022 there were eleven publications that year. Table 1 shows the 33 publications by year.
Table 1
Publication records and percentages by publication year.
|
Year |
Publication |
% of 33 |
|
2023 |
6 |
18.18 |
|
2022 |
11 |
33.33 |
|
2021 |
5 |
15.15 |
|
2020 |
6 |
18.18 |
|
2019 |
2 |
6.06 |
|
2018 |
1 |
3.03 |
|
2017 |
1 |
3.03 |
|
2016 |
0 |
0 |
|
2015 |
0 |
0 |
|
2014 |
0 |
0 |
|
2013 |
0 |
0 |
|
2012 |
1 |
3.03 |
The table indicates a notable pattern regarding research publications on the topic. In 2012, only one publication was recorded, suggesting a relatively low level of researcher interest during that period. Furthermore, from 2013 to 2016, no publications were observed, indicating a significant gap in scholarly attention during those years. However, in 2022, there was a notable surge in research activity, with 11 publications, signaling a marked increase in momentum and interest in the field.
QUALITY, QUANTITY, AND STRUCTURAL INDICATORS
This bibliometric study adopts a comprehensive approach employing quality, quantity, and structure indicators as outlined by (Merigó et al., 2015). Then, in order, to assess the productivity of authors, journals, institutions, or countries in terms of the number of publications, we employ quantity indicators. Quality indicators are essential for evaluating the impact and influence of authors, articles, or journals by assessing the frequency of their citations in other publications. Additionally, structural indicators are utilized to measure the connectivity and relationships among our selected publications.
DESCRIPTIVE ANALYSIS
In this study, a total of 33 publications were collected and analyzed from the Scopus core collection. Table 2 differentiates the 33 chosen publications between research articles and conference and review publications. A total of 31 of the publications were research articles.
Table 2
Document types record and percentage.
|
Document Type |
Records |
% of 33 |
|
Articles |
31 |
93.93 |
|
Conference Review |
1 |
3.03 |
|
Review |
1 |
3.03 |
Table 3 differentiates the chosen publications by discipline. More than half the publications were in business management. The others were in environmental science and general social sciences.
Table 3
Documents by subject area.
|
Subject area |
Records |
% of 33 |
|
Business Management |
17 |
51.51 |
|
Environmental Science |
10 |
30.30 |
|
Social Science |
6 |
18.18 |
FINDINGS
EVOLUTION OF SERVANT LEADERSHIP RESEARCH
To address our first research question on the evolution of servant leadership, we conducted a comprehensive timeline analysis of our 33 selected publications (there referred to as “documents”) on green servant leadership research from 2012 to 2023. There was a significant variation in the number of publications in Scopus over this time. Based on this variation, we identified two distinct research stages in the field: the pre-expansion stage and the expansion stage. Figure 1 illustrates that the 2012-2016 period comprised the pre-expansion stage, with only one publication. The 2016-2023 period had 32 publications, thus, we call it the expansion stage.
Figure 1
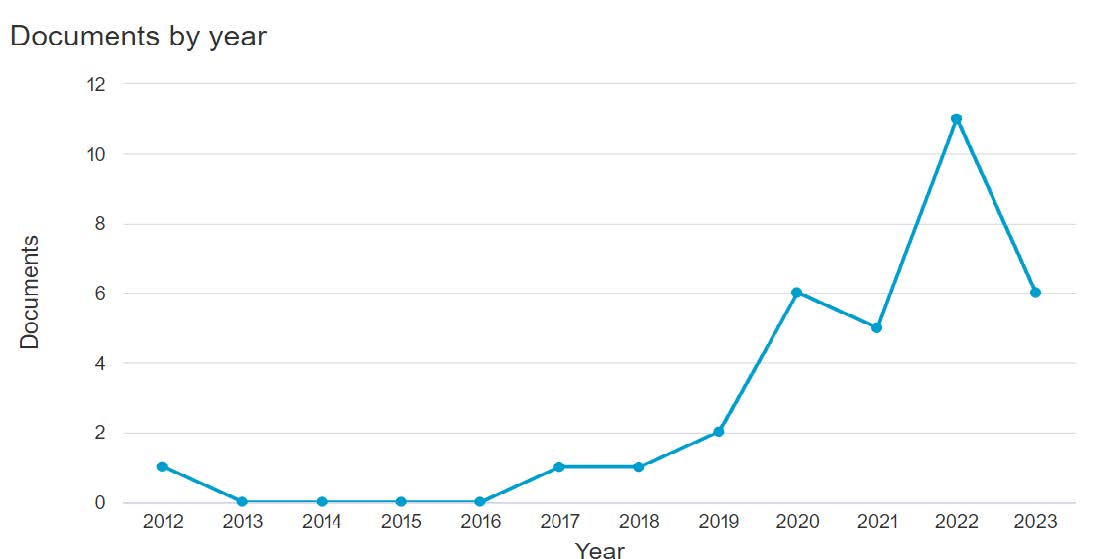
The surge in research output in the expansion stage suggests a significant increase in attention toward and interest in the topic of green servant leadership. The expansion period likely saw advancements in the understanding and exploration of green servant leadership, leading to a greater volume of scholarly contributions. Overall, the transition from the pre-expansion stage to the expansion period signifies a notable shift in the research landscape, reflecting heightened interest and engagement in the field of green servant leadership among researchers.
KEYWORDS
To explore our first and second research questions, we analyzed co-occurring author key words. The aim was to identify the primary focus areas within the field of green servant leadership research.
Figure 2 presents the density visualization depicting the results of the co-occurrence analysis of author keywords. This visualization provides a clear representation of the patterns and frequencies of the keywords within the context of servant leadership research. Out of a total of 111 keywords, only eight keywords met the criteria of having a minimum frequency of three occurrences. The total strength of co-author links with other keywords was analyzed specifically for the eight shortlisted keywords used by authors. This analysis aimed to examine the level of association and interconnectedness between these keywords and other terms within the context of servant leadership research. A stronger link between terms can be inferred when they are in closer proximity to each other. In the context of our analysis, the closeness of terms indicates a higher level of association and interconnectedness between them within the field of servant leadership research.
Figure 2
Density visualization of co-occurring author keywords in selected publications.
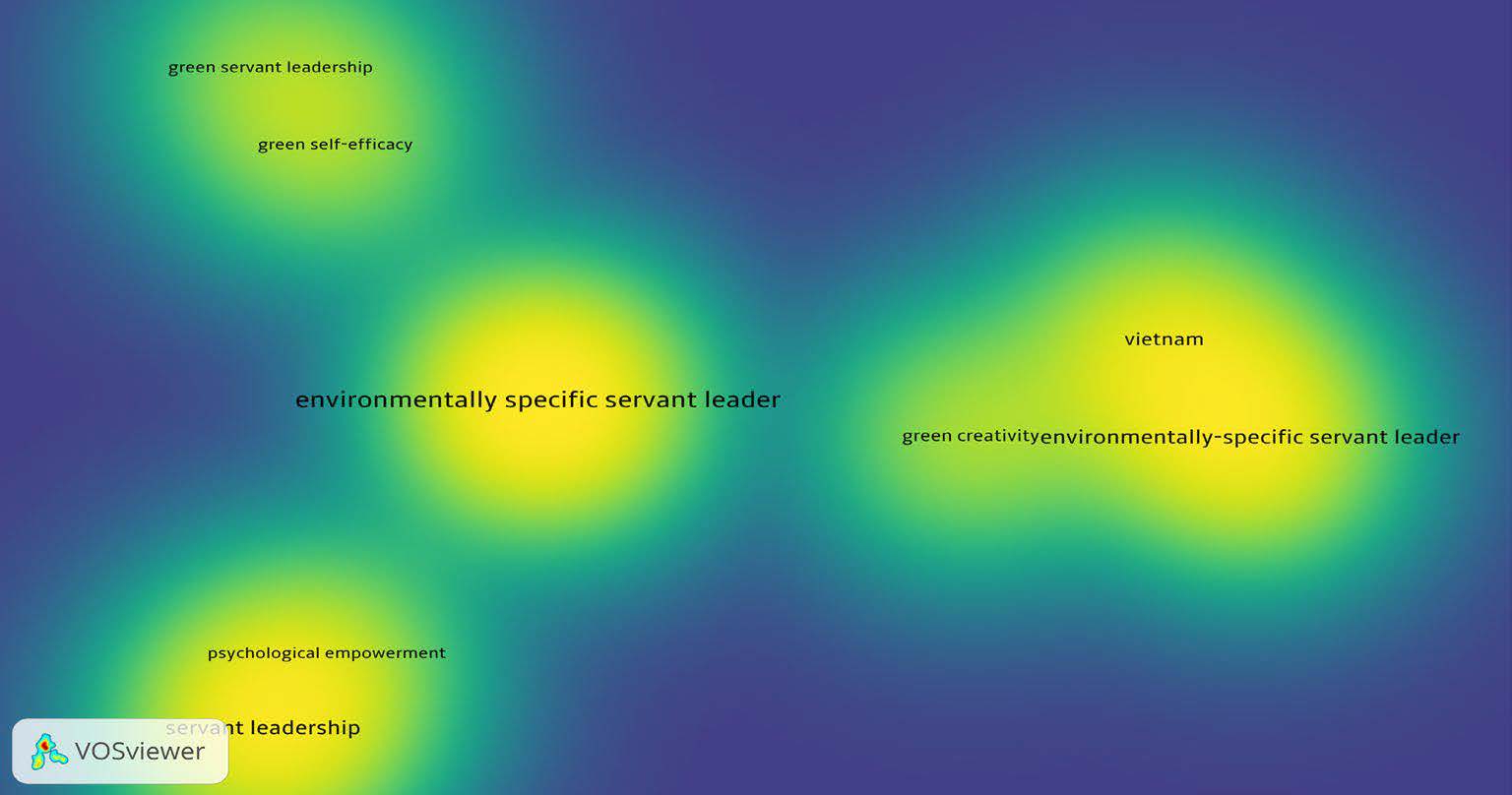
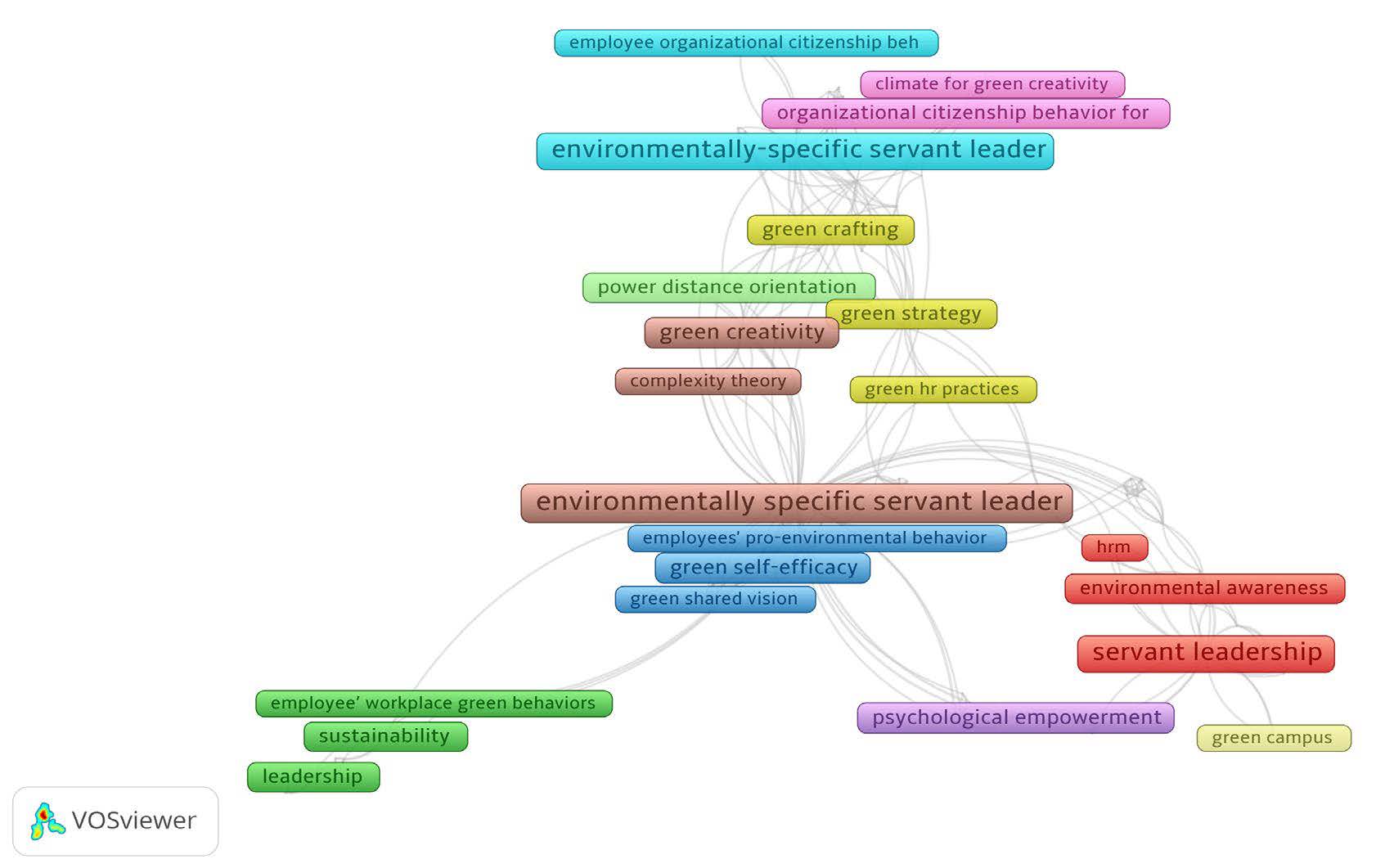
Figure 3 depicts a network visualization representing the author keywords. Three distinct clusters can be observed: red, green, and blue nodes. The red cluster in the network visualization represents keywords that are associated with the antecedents and outcome variables of green servant leadership. The green cluster in the network visualization consists of keywords that represent other leadership styles that researchers have studied in conjunction with servant leadership. whereas the blue cluster in the network visualization represents servant leadership research focused on organizational variables.
Figure 3
Network visualization of author keywords.
BIBLIOGRAPHIC COUPLING
To address our third research question regarding the research dynamics of green servant leadership, we utilized the bibliometric coupling algorithm. This algorithm was employed to identify influential authors, journals, publications, countries, and institutions within the field of servant leadership research.
COUNTRY AUTHORSHIP
To determine the most influential countries driving servant leadership research, and co-authorship across nation states, we conducted a bibliographic coupling analysis examining connections and overlaps in the bibliographic references of our selected publications. The countries with a high degree of bibliographic coupling have made significant contributions to the development and advancement of green servant leadership as a research field. Figure 4 shows the details of the countries.
Figure 4
Overlay visualization by country.
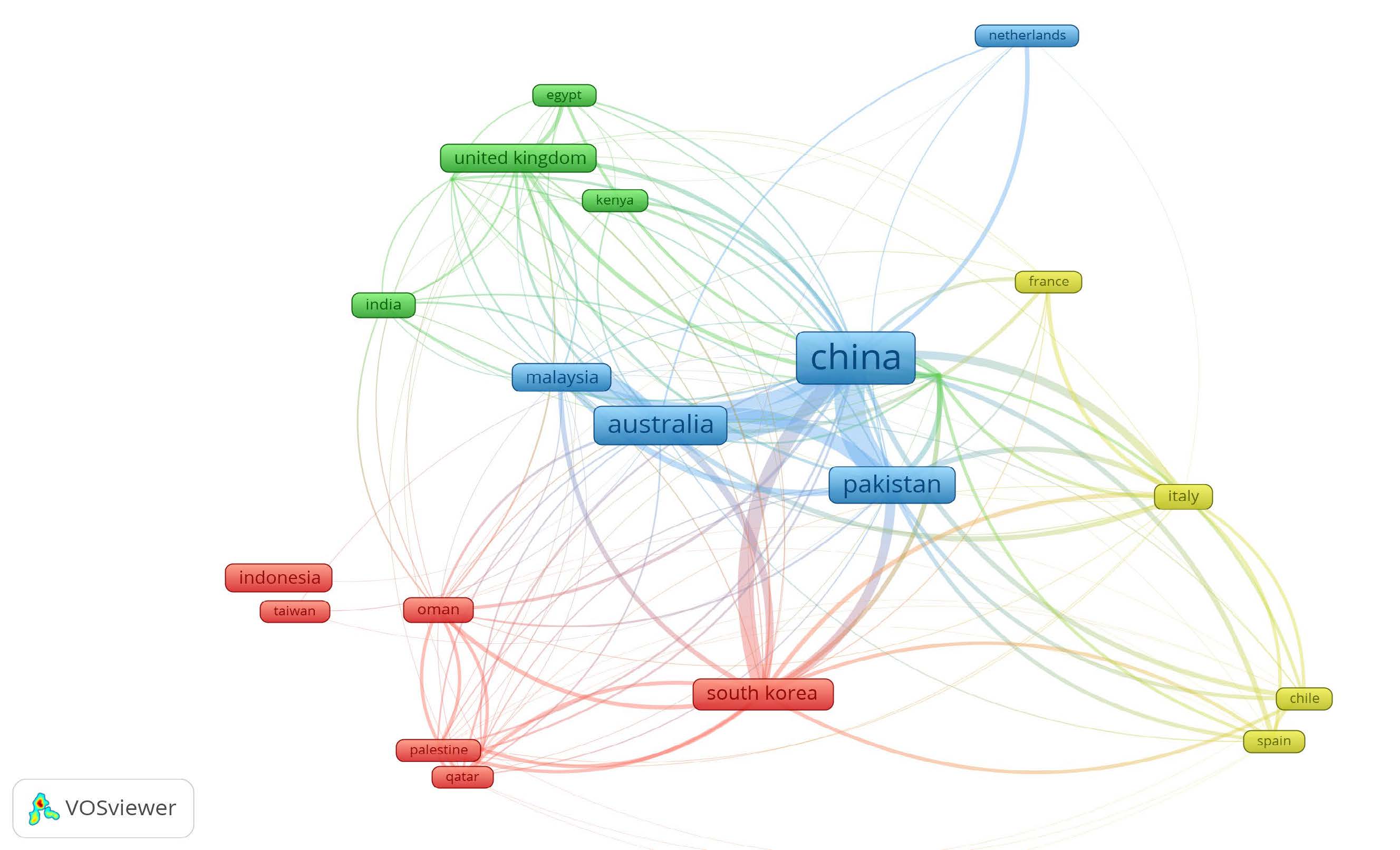
Our analysis unveiled China as the most prominent contributor to green servant leadership research, boasting 14 publications and a cumulative link strength of 4,467. Australia was second with eight publications and a link strength of 2,952. Pakistan and South Korea occupied the third and fourth positions respectively, with seven and four publications each. Their respective link strengths were 3,038 for Pakistan and 2,316 for South Korea.
CO-AUTHORSHIP
Figure 5 depicts the results of the bibliographic coupling analysis conducted at the author level, with a threshold of three publications per author. Among the total of 102 authors, eight authors met the threshold criteria. The total strength of each author was computed by aggregating their bibliographic coupling scores. Based on these scores, the authors were ranked accordingly. The author T. T. Luu emerged as the foremost contributor in the domain of green servant leadership, boasting a notable record of ten publications. Furthermore, their publications garnered a total of 527 citations and a cumulative link strength of 1,875. This signifies the significant scholarly impact and influence of this scholar’s contributions to the field of green servant leadership research.
Figure 5
Overlay visualization by author.

Table 4 provides a comprehensive overview of the number of publications, citations, and total strength for each of the eight authors shortlisted through the bibliographic coupling analysis. These findings provide a clear overview of the scholarly contributions and impact of each author in the field of servant leadership research.
Table 4
Scholars and their contribution to the field.
|
Author |
Publications |
Total Citations |
Link Strength |
|
T. T. Luu |
10 |
527 |
1875 |
|
F. Ahmed |
8 |
320 |
1843 |
|
N. A. Faraz |
6 |
255 |
1656 |
|
M. Ying |
3 |
220 |
1576 |
|
M. Aboramadan |
3 |
195 |
1551 |
|
J. A. Ho |
1 |
98 |
1551 |
|
H. Zafar |
1 |
75 |
1480 |
|
L. T. Tuan |
1 |
60 |
1154 |
CO-AUTHORSHIP NETWORK ACROSS THE GLOBE
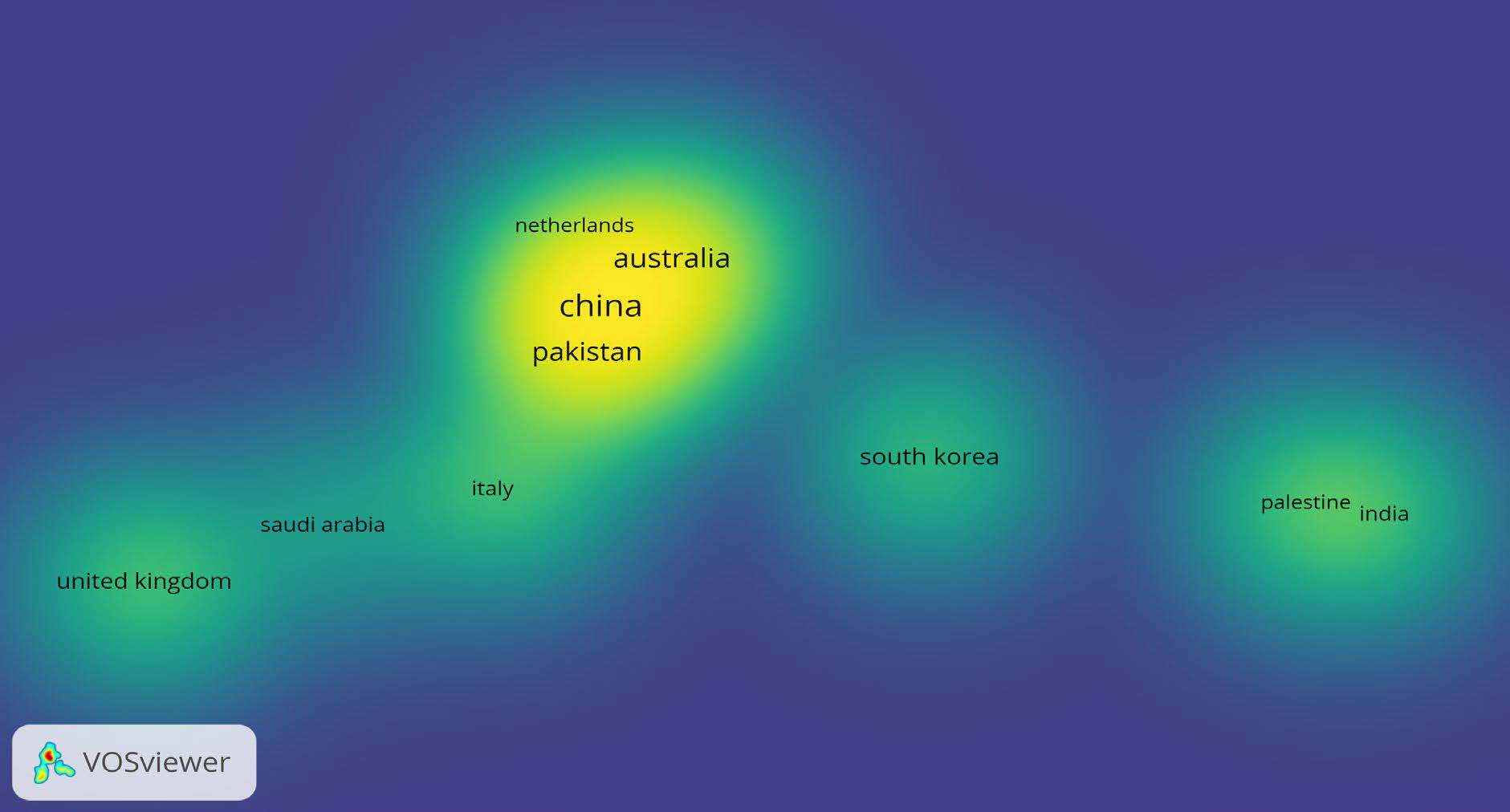
To investigate the fourth research question, we conducted a co-authorship analysis at the country level. This analysis aimed to examine the collaborative patterns among authors from different countries within the research field. By using countries as the unit of analysis, we were able to explore how authors from various nations have collaborated in this research area. Each cluster in the analysis represents the collaboration among authors in researching the topic of green servant leadership.
Figure 6 illustrates clusters representing global co-authorship patterns. These clusters have emerged based on their total link strength, indicating the strength of collaboration among authors. The dense cluster between Australia, China, Pakistan, and the Netherlands indicates that authors from these countries have collaborated well. These findings offer insights into the global network of collaborative efforts in advancing green servant leadership research across various regions.
Figure 6
Density visualization based on co-authorship across the globe.
DISCUSSION
Our analysis, based on 33 publications selected from Scopus, suggests that China is the most influential country in the field of green servant leadership research, exhibiting a significant lead over other countries such as Australia, Pakistan, South Korea, and Malaysia. The author T. T. Luu emerged as the most influential author in green servant leadership. T. T. Luu had the highest number of citations and the strongest total link strength, indicating significant recognition and impact within the research community. Second and third were F. Ahmed, and N. A. Faraz. These authors have demonstrated substantial contributions and recognition in green servant leadership. The most influential field in terms of publications by far was business management.
There has clearly been research conducted from different parts of the world on various aspects of green servant leadership. In recent years, there has been a notable surge in the momentum of green servant leadership research. But the field is still in its infancy and the term “green servant leadership” is new. The co-author analysis conducted between different countries revealed not only collaborations within individual countries but also international collaborations among researchers in the field of green servant leadership research. Most of the existing research on green servant leadership has focused on the contexts of Australia, China, and Pakistan. There are few scholars from African, Middle Eastern, and South Asian countries, or work focused on those contexts.
This study’s results serve as a valuable guide for researchers and scholars interested in further exploring the research area of servant leadership within the field of social sciences. In addition, this study facilitates researchers identifying and establishing networks and collaborations with other institutions, countries, and authors from around the world who have are researching servant leadership. To advance the field of green servant leadership, researchers should focus on exploring underrepresented contexts such as Africa, the Middle East, and South Asia, examining how cultural, social, and economic factors influence the adoption and effectiveness of green servant leadership practices. Longitudinal studies tracking the evolution and impact of these practices over time, interdisciplinary collaboration to integrate insights from diverse fields, and comparative cross-cultural studies are essential. Additionally, developing practical frameworks for implementing green servant leadership, robust measures for evaluation, and integrating these principles into leadership development programs can bridge the gap between research and practice, fostering sustainable development and responsible leadership globally.
CONCLUSION
This study provides valuable bibliometric insights into research on green servant leadership. It catalogues publications through author keywords, co-authorship patterns among countries, and bibliographic coupling across different dimensions. The dominance of China in green servant leadership research underscores its significant contributions and influence in shaping the discourse within this domain. The prominence of authors like T. T. Luu and F. Ahmed reflects the caliber of their contributions and the recognition they have garnered within the research community. Furthermore, the surge in momentum observed in recent years signifies the growing interest and relevance of green servant leadership as a research topic.
Overall, the structured and objective examination of the literature presented in this study offers valuable guidance for researchers and scholars interested in delving deeper into the realm of servant leadership within the social sciences. The findings serve as a foundation for establishing networks and collaborations across institutions and countries, thereby fostering continued advancements and innovations in the field of green servant leadership research. While other bibliometric analyses of green servant leadership exist, including information on citation patterns and key contributors, like this one, they often lack in-depth qualitative analysis. Additionally, there is a need for more comprehensive coverage of diverse perspectives and regions, as well as exploration of emerging themes within the field. Our reliance on quantitative metrics may overlook the contextual nuances and practical implications of the green servant leadership literature. Future studies should aim to address these limitations by integrating qualitative approaches, considering a broader range of sources, and providing more nuanced interpretations of the data.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors acknowledge the Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, UTM Encouragement Research, VOT Q.J130000.3829.31J18, and R.J 130000.7629.4C787 for their financial support.
REFERENCES
Afsar, B., Cheema, S., & Javed, F. (2018). Activating employee’s pro‐environmental behaviors: The role of CSR, organizational identification, and environmentally specific servant leadership. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 25(5), 904-911.
Afsar, B., Maqsoom, A., Shahjehan, A., Afridi, S. A., Nawaz, A., & Fazliani, H. (2020). Responsible leadership and employee’s proenvironmental behavior: The role of organizational commitment, green shared vision, and internal environmental locus of control. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 27(1), 297-312.
Cobo, M. J., López‐Herrera, A. G., Herrera‐Viedma, E., & Herrera, F. (2011). Science mapping software tools: Review, analysis, and cooperative study among tools. Journal of the American Society for information Science and Technology, 62(7), 1382-1402.
Ehrhart, M. G. (2004). Leadership and procedural justice climate as antecedents of unit‐level organizational citizenship behavior. Personnel Psychology, 57(1), 61-94.
Eva, N., Robin, M., Sendjaya, S., van Dierendonck, D., & Liden, R. C. (2019). Servant leadership: A systematic review and call for future research. The Leadership Quarterly, 30(1), 111-132.
Fahimnia, B., Sarkis, J., & Davarzani, H. (2015). Green supply chain management: A review and bibliometric analysis. International Journal of Production Economics, 162, 101-114.
Greenleaf, R. K. (1970). The Servant as Leader. Robert K. Greenleaf Center.
Greenleaf, R. K. (2002). Servant Leadership: A Journey into the Nature of Legitimate Power and Greatness. Paulist Press.
Hoch, J. E., Bommer, W. H., Dulebohn, J. H., & Wu, D. (2018). Do ethical, authentic, and servant leadership explain variance above and beyond transformational leadership? A meta-analysis. Journal of Management, 44(2), 501-529.
Hussain, N., Zakuan, N., Yaacob, T., Hashim, H., & Hasan, M. (2023). Employee green behavior at workplace: A review and bibliometric analysis. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 13(3), 1679-1690.
Karakas, F., & Sarigollu, E. (2013). The role of leadership in creating virtuous and compassionate organizations: Narratives of benevolent leadership in an Anatolian tiger. Journal of Business Ethics, 113, 663-678.
Lee, M.-H., Lin, C., Lin, C.-K., & Lu, W.-Y. (2014). Moderating effect of institutional responsiveness on the relationship between green leadership and green competitiveness. Social Behavior and Personality: an International Journal, 42(9), 1483-1494.
Liden, R. C., Wayne, S. J., Liao, C., & Meuser, J. D. (2014). Servant leadership and serving culture: Influence on individual and unit performance. Academy of Management Journal, 57(5), 1434-1452.
Liden, R. C., Wayne, S. J., Meuser, J. D., Hu, J., Wu, J., & Liao, C. (2015). Servant leadership: Validation of a short form of the SL-28. The Leadership Quarterly, 26(2), 254-269.
Manz, C. C., Manz, K. P., Adams, S. B., & Shipper, F. (2011). Sustainable performance with values‐based shared leadership: a case study of a virtuous organization. Canadian Journal of Administrative Sciences/Revue Canadienne des Sciences de l'Administration, 28(3), 284-296.
Merigó, J. M., Gil-Lafuente, A. M., & Yager, R. R. (2015). An overview of fuzzy research with bibliometric indicators. Applied Soft Computing, 27, 420–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2014.10.035
Miller, D., & Friesen, P. H. (1983). Strategy‐making and environment: the third link. Strategic Management Journal, 4(3), 221-235.
Neubert, M. J., Hunter, E. M., & Tolentino, R. C. (2016). A servant leader and their stakeholders: When does organizational structure enhance a leader’s influence? The Leadership Quarterly, 27(6), 896-910.
Paesen, H., Wouters, K., & Maesschalck, J. (2019). Servant leaders, ethical followers? The effect of servant leadership on employee deviance. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 40(5), 624-646.
Robertson, J. L., & Barling, J. (2017). Contrasting the nature and effects of environmentally specific and general transformational leadership. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 38(1), 22-41.
Schaubroeck, J., Lam, S. S., & Peng, A. C. (2011). Cognition-based and affect-based trust as mediators of leader behavior influences on team performance. Journal of Applied Psychology, 96(4), 863.
Sher, S., & Nawaz, S. (2021). Impact of Green Servant Leadership on Organizational Sustainability: The Mediating Role of Green Human Resource Management Practices. iRASD Journal of Management, 3(3), 448-457.
Siddiquei, A., Asmai, F., Asadullah, M. A. & Mir, F. 2021. Environmental-specific servant leadership as a strategic tool to accomplish environmental performance: A case of China. International Journal of Manpower, 42, 1161-1182.
Sosik, J. J., & Jung, D. (2011). Full Range Leadership Development: Pathways for People, Profit and Planet. Taylor & Francis.
Spears, L. C. (Ed.). (1995). Reflections on leadership: How Robert K. Greenleaf’s theory of servant-leadership influenced today’s top management thinkers. Wiley.
Tuan, L. T. (2018). Activating tourists’ citizenship behavior for the environment: the roles of CSR and frontline employees’ citizenship behavior for the environment. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 26(7), 1178-1203.
Tuan, L. T. (2020). Environmentally-specific servant leadership and green creativity among tourism employees: Dual mediation paths. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 28(1), 86-109.
Tuan, L. T. (2021). Effects of environmentally-specific servant leadership on green performance via green climate and green crafting. Asia Pacific Journal of Management, 38(3), 925-953.
van Dierendonck, D. (2011). Servant leadership: A review and synthesis. Journal of Management, 37(4), 1228-1261.
van Dierendonck, D., Stam, D., Boersma, P., de Windt, N., & Alkema, J. (2014). Same difference? Exploring the differential mechanisms linking servant leadership and transformational leadership to follower outcomes. The Leadership Quarterly, 25(3), 544-562.
van Eck, N., & Waltman, L. (2010). Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics, 84(2), 523-538.
Whittington, J. L. (2017). Creating a Positive Organization Through Servant Leadership. In C. J. Davis (Ed.), Servant Leadership and Followership: Examining the Impact on Workplace Behavior (pp. 51–79). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-59366-1_3
Zupic, I., & Čater, T. (2015). Bibliometric Methods in Management and Organization. Organizational Research Methods, 18(3), 429–472. https://doi.org/10.1177/
1094428114562629
