Natural and Life Sciences Communications
Instructions for Preparation of Manuscripts
Types of Articles and Formats
Manuscripts submitted to Natural and Life Sciences Communications are critically reviewed by at least 2 reviewers using the double-blinded review systems before they can be published. The reviewer has the major responsibility for critical evaluation to determine whether or not a manuscript meets standards of scientific and literary quality. Reviews must be based on manuscripts of satisfactory literary quality. It is not the task of a reviewer to edit poorly prepared papers or to correct readily detectable errors. In order to avoid any embarrassment to authors, any undue burden for reviewers or editors, or any loss of time and effort, every paper should have a thorough preliminary review by competent colleagues of the author before it is sent to the journal.
| Manuscript submission |
Natural and Life Sciences Communications is an online journal that welcomes only English articles. English manuscripts must be written in “Times New Roman” font of 12-point type. The required font type must be used along with double spacing between lines of text, and continuous line numbering along the margins of the manuscript. Manuscripts can be of any length. There are no restrictions on the number of words or a number of tables and figures.
Importantly, English articles from corresponding authors do not belong to the English native speaker, while authors must send a supplemental document confirming that the article was proofread by a qualified native English speaker or authorized organization.
Manuscripts have to be submitted through the journal’s online submission system at ScholarOne Manuscripts (manuscriptcentral.com) |
| Type of Manuscript |
Research articles; Reports of original research that have never been published elsewhere. The manuscript should be composed and organized according to the required sequence: 1. title page (Titles, Author names, Affiliations, Email addresses of correspondence, Acknowledgments, Funding, Author contribution) 2. main text (Titles, Abstract, Keywords, Introduction, Materials and Methods, Results, Discussion, Conclusion, Conflict of Interest, References, Tables, and Figure). Abstracts should be a maximum of 250 words and 5 keywords. There is no word limit on the manuscript and no limit to the number of figures, tables, and references.
Review articles; The literature reviews, systematic reviews, market reviews, and critical reviews will be accepted for consideration. Critical, comprehensive, and specific papers presenting issues of interest or topics of significant academic value. Although the main text structure may vary based on the review subtopics, content should be organized in the same manner as a research article. Guideline for Review Article 1. The first author or corresponding author must have at least an h-index of 10. 2. The review must be informative and concise, critical and in-depth, address novel aspects or concepts, provide future perspectives, and must attract a wide readership. 3. The authors must have experience in the subject of the Review and can demonstrate this expertise through at least a few original publications. 4. The journal will generally not consider Review articles from postgraduate students or authors who fail to show his/her expertise on the subject. 5. At least 50% of the cited references should not be older than 5 years.
Authors who are with this guideline are welcome to send an email to the Editor-in-Chief, Dr. Wasu Pathom-aree, by e-mail (wasu.p@cmu.ac.th) with the following documents: (1) The title of the proposed Review (must be short and concise; Keywords no more than 8). (2) An abstract of the proposed Review (This must be no more than 250 words). (3) The CV with a publication list, please mark the original publications that are related to the topic of the proposed Review. (4) Outline in detail the novelty of the proposed Review. (5) Please explain the difference between the proposed Review with related previous published reviews.
Short communications; Research reports of concise nature determined by the limitations of the study or based on a very new idea and/or controversial issue, etc. The material should present complete, original, and new findings that emphasize specific research issues. The format must be similar to the original research article but presented as a brief report. Intended as a short format, these articles should be a maximum of 2,000 words (excluded references), limited to 2 figures and 2 tables, and a maximum of 20 references. |
| Cover letter |
A cover letter from the corresponding author is required assuring that the article has never before been published and is also not under consideration for publication elsewhere. The cover letter should include the following information;
|
| Manuscripts Format |
All manuscripts must be in English. Manuscripts must follow accepted practice in the natural sciences as detailed in the CSE Manual for Authors, Editors and Publishers (by the Council of Science Editors and formally known as the CBE Manual of Style). The manuscript should not exceed 30 double-spaced A4 pages (Time New Roman or similar font, size 12”, with 1” margins). The manuscripts must be made available in MS Word format.
|
| Manuscript should be organized in the following order |
Two separate files need for submission, a Title page file (included author information) and Main manuscript file (without author information).
1st file-- Title page file 1. Title The author should design his title to supply enough information for the potential reader to make a reliable decision as to whether the paper is of probable interest. 2. Author(s) Name(s) of author(s), complete postal address(es), and country of affiliations and E-mail of the corresponding author. 3. ORCID iD (All required, if available) 4. Acknowledgement Any acknowledgements should be typed as text. 5. Author contribution 5.1 Credit Classification Please follow the term and definition of CRediT author statement via link: https://www.elsevier.com/researcher/author/policies-and-guidelines/credit-author-statement 5.2 Level of Contribution: The CRediT system allows authors to specify the nature of their contributions to a research project using standardized roles. To give more details, Natural and Life Sciences Communications allows authors to indicate the Level of contribution for each role using the following three terms:
These levels help clarify who did what, increasing transparency and ensuring appropriate recognition—especially important for multidisciplinary and collaborative work. For transparency, we encourage authors to submit an author statement file outlining their individual contributions to the paper. 6. Conflict of interest All authors must disclose any financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence (bias) their work. 7. Funding (optional) Any funding should be typed as text.
2nd file-- Main manuscript file 1. Title The author should design his title to supply enough information for the potential reader to make a reliable decision as to whether the paper is of probable interest. 2. Key Contribution The breakthroughs or highlights of the manuscript. Authors can write one or two sentences to describe the most important part of the paper. 3. Highlights (Optional) Highlights should include 3 to 5 bullet points (maximum 85 characters, including spaces, per bullet point). 4. Graphical Abstract: A graphical abstract (GA) is required. Its use is encouraged as it draws more attention to online articles. GA should summarize the contents of the article in a concise, pictorial form designed to capture the attention of a wide readership. GA should be a high-quality illustration or diagram in any of the following formats: PNG, JPEG, TIFF, or SVG. Written text in a GA should be clear and easy to read, using Times New Roman. The minimum required size for the GA is 560 × 1100 pixels (height × width). The size should be of high quality in order to reproduce well at 300 dpi for color and at 1200 dpi for black and white. 5. Abstract and Keywords The abstract should be a suitable literary adjunct to the scientific report and it should meet the needs of the literary researcher or information specialist. The length of the abstract should not exceed 250 words for full-length papers. Keywords for indexing should be listed at the end of the abstract. 6. Introduction Introductions should be kept short. Good introductions should include: (i) brief statement of the problem that justifies doing the work or of the hypothesis on which it is based; (ii) the findings of others that will be challenged or developed; and (iii) an explanation of the general approach and objectives. The aim of the introduction should be to excite and interest the reader. 7. Materials and Methods This section contains details about materials, techniques, experimental design, and environment. Sufficient detail should be provided to permit the reader to repeat the experiments. The methods section may be arranged in a chronological pattern, succession of techniques, or other manners which will most effectively assist the reader in studying the paper 8. Results Use tables, graphs, diagrams, and photographs to provide a clear understanding of the results. Data included in illustrations and tables should not be discussed extensively in the text, but significant findings should be pointed out. Show how the objectives have been achieved. The results should be connected to one another. 9. Discussion In the discussion section the author assesses the meaning of the results. Show how the results provide a solution to the problem stated in the introduction or given as the objective. Connect the work of this study with previous works showing how and why they differ or agree. Point out the significance and implications of the work and indicate possible future developments. Do not give excuses for unexpected results and failures of experiment. Controversial issues should be discussed clearly and fairly. Where results differ from previous results, they should be explained. 10. Conclusion Some papers have a conclusion section. This includes any significant conclusions that have been drawn from the work. These should be carefully worded so there is no misunderstanding on the part of the reader. It is often desirable to present conclusions as part of the discussion section; however, in a paper that is long and complex, it may be helpful to summarize conclusions in a separate section.
11. References All in-text citations, footnotes/endnotes, and the reference page must follow the CSE guidelines. Samples from these guidelines can be found http://cmuj.cmu.ac.th
11.1 In-text citations The form used for giving the reference in the text will vary according to the construction of the sentence in which it occurs, e.g., Bell (1999) or (Bell, 1999). When there are two authors, name both of them, e.g., Heimann and Willmann (1998) or (Heimann and Willmann, 1998). When there are three or more authors, cite their paper in the form Hildebrandt et al., (1999) or (Hildebrandt et al., 1999). If two or more articles by the same author or authors in the same year are cited, they should be designated as follow: Pandey et al., (1984a, 1984b, 1984c).
11.2 Reference list All citations, whether to published literature or to unpublished work are to be listed alphabetically by surname of senior author at the end of the manuscript. Each reference to a periodical publication must include, in order, the name(s) of the author(s), the year of publication, the full title of the article, the publication in which it appears, the volume and inclusive page numbers, and the digital object identifier (DOI), if available. The reference lists are based on the CSE Manual for Authors, Editors and Publishers (by the Council of Science Editors and formally known as the CBE Manual of Style). Journal article Halmilton, M.B., Pincus, E.L., Fion, A.D., and Fleischer, R.C. 1999. Universal linker and ligation procedures for construction of genomic DNA libraries enriched for microsatellites. Biotechniques. 27: 500-507.
Book Sokal, R.R., and Rohlf, F.J. 1995. Biometry: The principles and practice of statistics in biological research. W.H. Freeman and Co, New York.
Chapter in book Jackson, M.B. 1982. Ethylene as a growth promoting hormone under flooded conditions. p.291-301. In P.F. Wareing (ed) Plant growth substance. Academic Press, London.
Edited proceeding, symposia etc. Pratt, A., Gilkes, R.J., Ward, S.C., and Jasper, D.A. 2000. Variations in the properties of regolith materials affect the performance of tree growth in rehabilitated bauxite mine-pits in the Darling Range, SW-Australia. p.87-88. In: Brion, A., and Bell, R.W. (eds) Proceeding of Remade Land 2000, the International Conference on Remediation and Management of Degraded Lands. Fremantle, 30 Nov-2 Dec 2000. Promaco Conventions, Canning Bridge.
Dissertation Senthong, C. 1979. Growth analysis in several peanut cultivars and the effect of peanut root-knot nematode (Meloidogyne arenaria) on peanut yields.Ph.D. Dissertation. University of Florida, Gainesville, Florida, USA.
|
| Reviewing |
Manuscripts submitted to Natural and Life Sciences Communications are critically reviewed by at least 2 reviewers using the double-blinded review systems before they can be published. The reviewer has the major responsibility for critical evaluation to determine whether or not a manuscript meets standards of scientific and literary quality. Reviews must be based on manuscripts of satisfactory literary quality. It is not the task of a reviewer to edit poorly prepared papers or to correct readily detectable errors. In order to avoid any embarrassment to authors, any undue burden for reviewers or editors, or any loss of time and effort, every paper should have a thorough preliminary review by competent colleagues of the author before it is sent to the journal. |
| "Declaration of generative AI use" policy |
Generative AI Use Declaration Policy Natural and Life Sciences Communications requires authors to declare any use of generative AI (AI Tools) during the preparation of their manuscript upon initial submission. The Role of AI Tools The journal recognizes that AI Tools can be valuable assets, helping researchers to:
Conditions for Responsible Use While authors are permitted to use AI Tools, this use is strictly subject to human oversight. AI should never replace the author's critical thinking, expertise, and evaluation. Author Responsibility and Accountability Authors are ultimately responsible and accountable for the entire content of their work. This includes:
Authorship Restriction AI Tools must not be listed or cited as an author or co-author on the manuscript, as authorship requires responsibilities that only humans can perform. Disclosure Requirement The required disclosure statement about AI Tool use must be added at the end of the manuscript in a new section before the references list when the paper is first submitted. This statement will be included in the published work. |
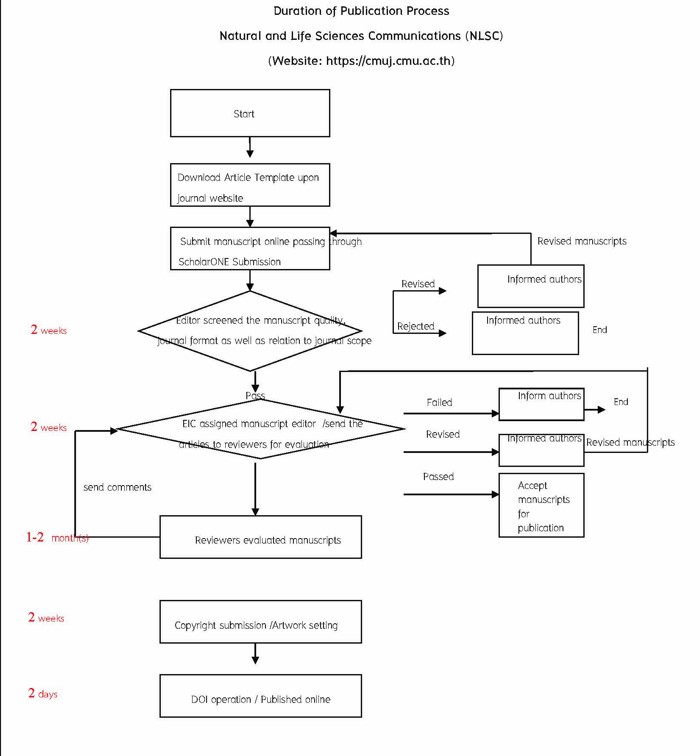
| Duration of Publication Process |
|